
Content hub

Revolutionizing Residency Training: Introducing the MAAS Program by AANA
In the realm of orthopedic education, the Arthroscopy Association of North America (AANA) has once again set a precedent with the launch of its Mobile Advanced Arthroscopy Simulator (MAAS) program in 2023. This innovative initiative has already made waves across various residency programs, showcasing its potential to redefine how surgical skills are acquired and honed.
Development and evaluation of a “simulator-based” ultrasound training program for university teaching in obstetrics and gynecology–the prospective GynSim study
This study addresses the challenges of ultrasound education in obstetrics and gynecology, focusing on the potential benefits of simulation techniques in medical training. Aiming to evaluate the impact of a structured simulator-based training program, this prospective, randomized, interventional study examines its effects on educational outcomes for 5th year medical students.
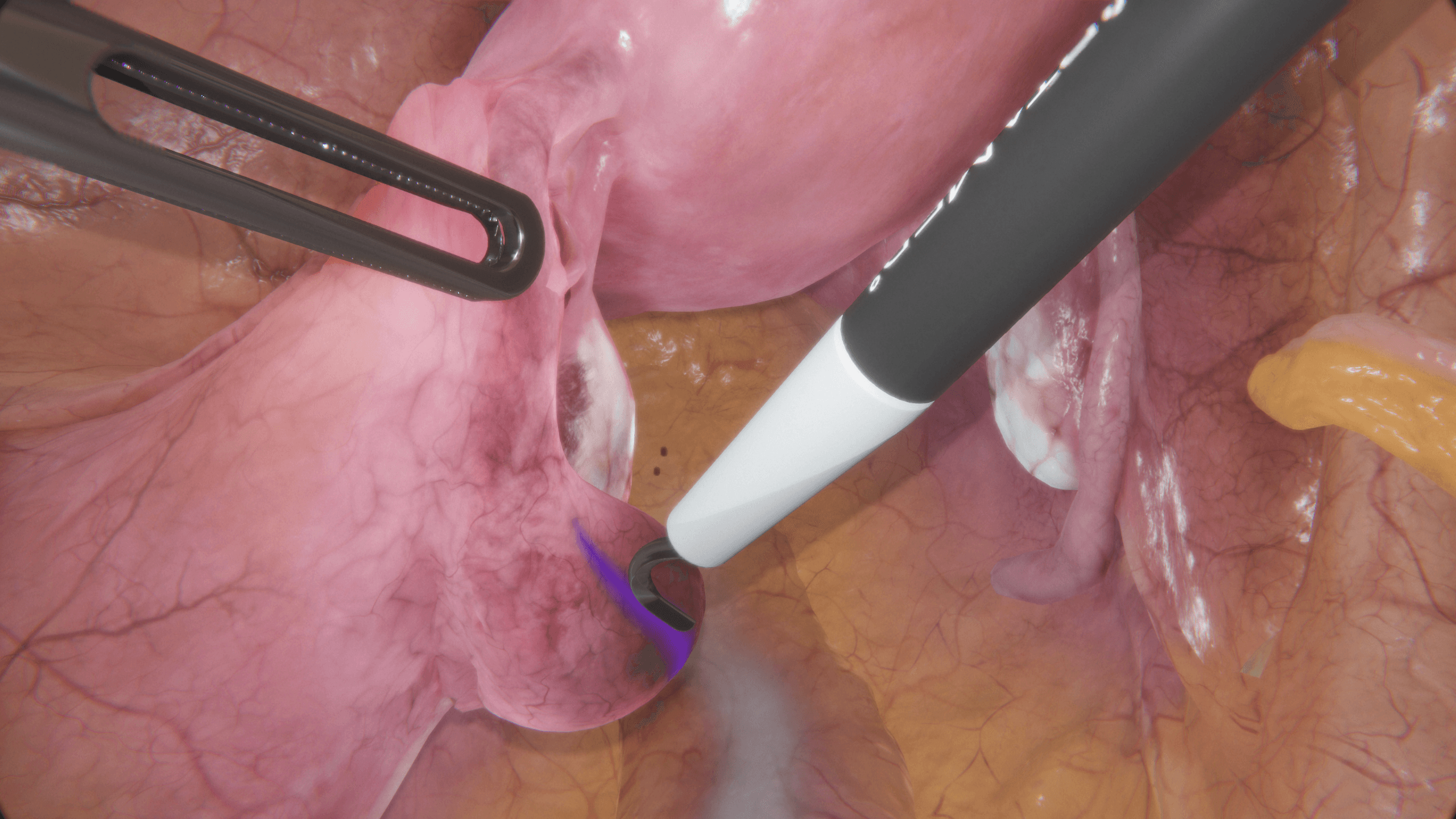
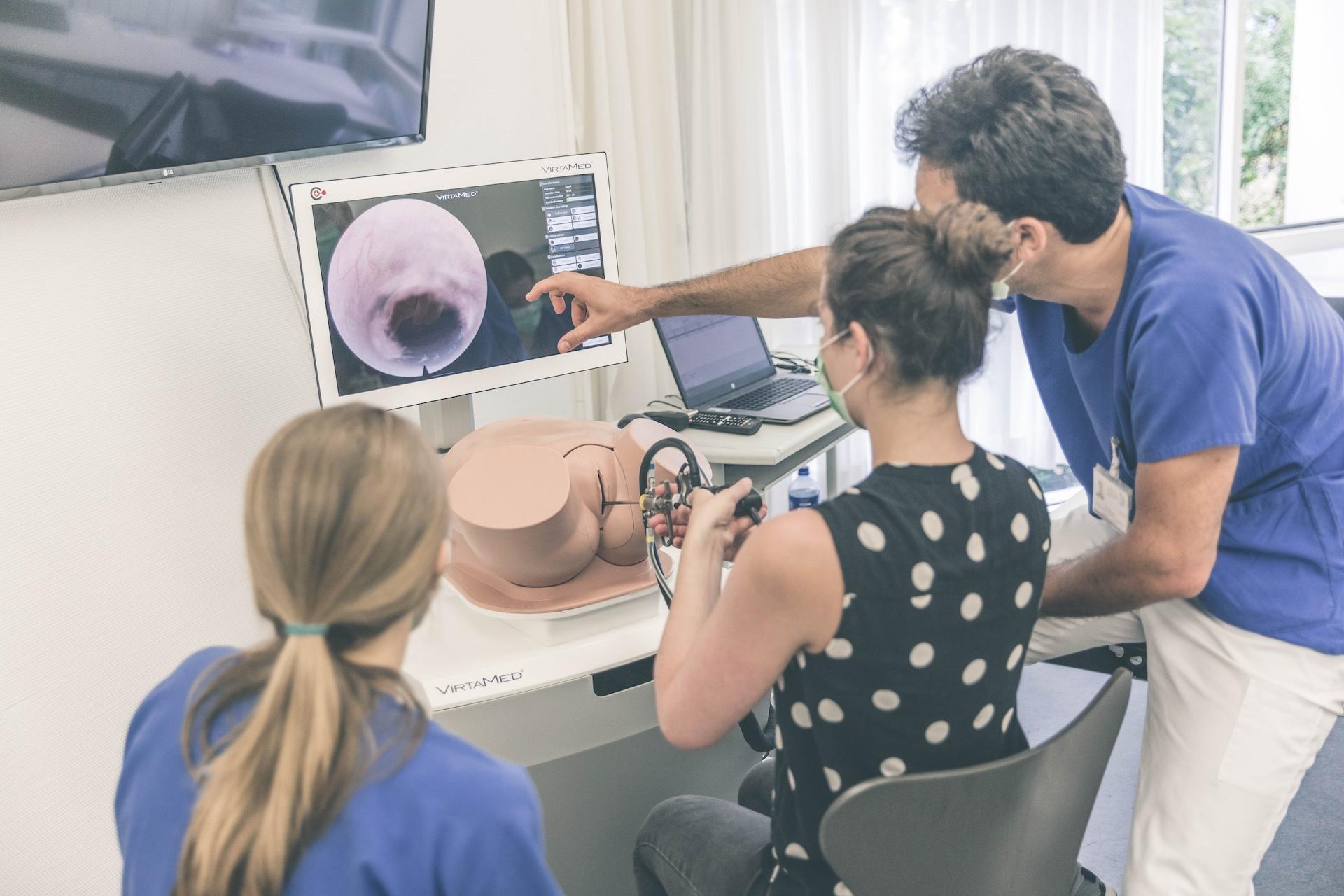
Tübingen University Hospital on VirtaMed Gynecological Laparoscopy Simulation: Enabling Systematic Structured Education
We asked experts from the Women's Health Clinic at Tübingen University Hospital in Germany, one of the leading centers of excellence collaborating with VirtaMed on LaparoS™ development, to share their impressions on the value that the mixed reality simulator brings to training and education of gynecology residents.
Ten hours of simulator training in arthroscopy are insufficient to reach the target level based on the Diagnostic Arthroscopic Skill Score
Our data have demonstrated that arthroscopic skills can be taught effectively on a simulator, but a 10-h course is not sufficient to reach the target level set by experienced arthroscopists. However, learning progress can be monitored more objectively during simulator training than in the operating room, and simulation may partially replace the current practice of arthroscopic training.
- Anetzberger H, Reppenhagen S, Eickhoff H, Seibert FJ, Döring B, Haasters F, Mohr M, Becker R. Ten hours of simulator training in arthroscopy are insufficient to reach the target level based on the Diagnostic Arthroscopic Skill Score. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Apr;30(4):1471-1479. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06648-y.
Surgical simulation training should become a mandatory part of orthopaedic education
This study suggests that surgical simulation training is well accepted and even demanded among surgical residents as an alternative training solution able to address some of the limitations and challenges of the current one-to-one apprenticeship model. There is a wide variation among the residents regarding the number of training hours required, underscoring the need for structured performance-based simulator training.
- Seil R, Hoeltgen C, Thomazeau H, Anetzberger H, Becker R. Surgical simulation training should become a mandatory part of orthopaedic education. J Exp Orthop. 2022 Feb 28;9(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40634-022-00455-1.
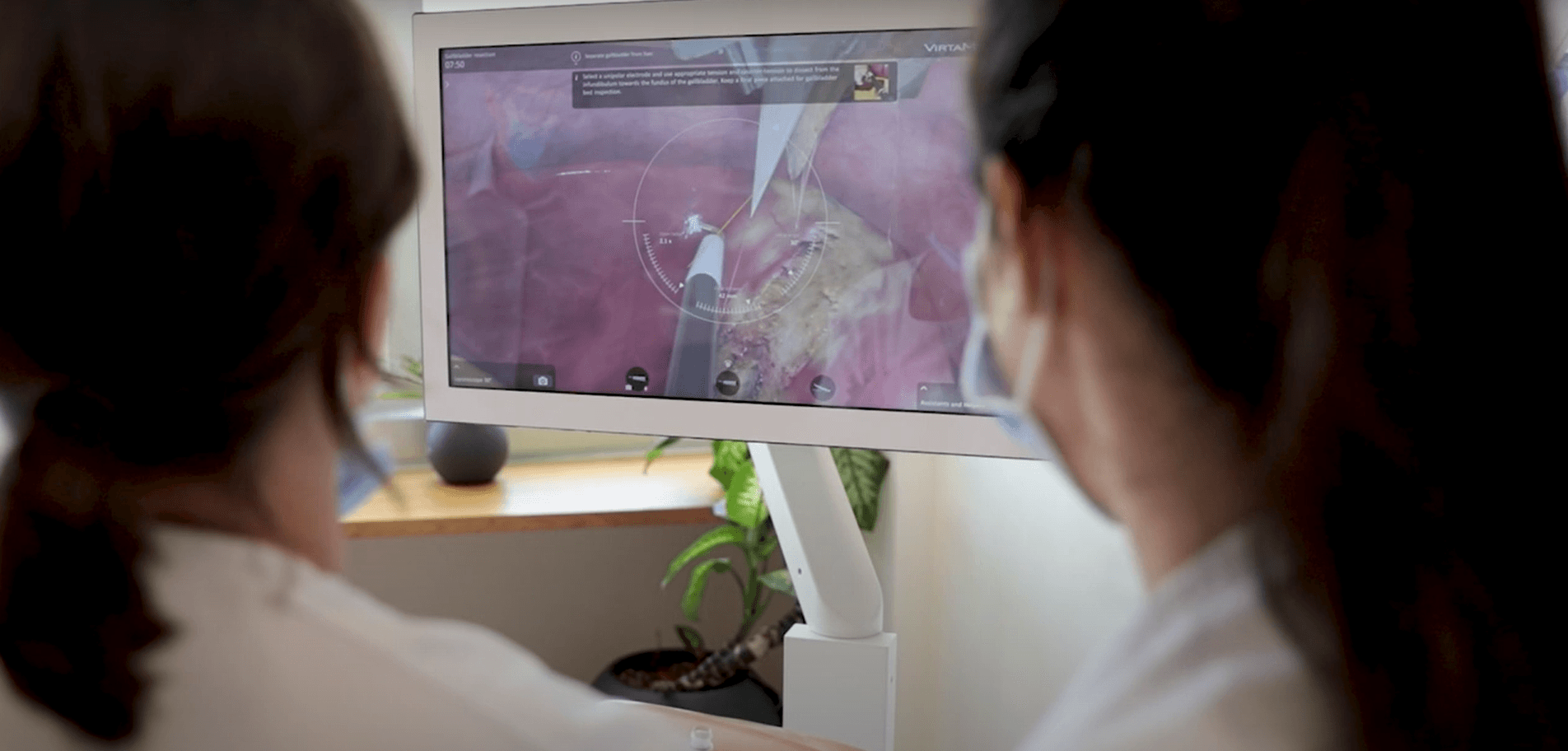
The Diagnostic Arthroscopy Skill Score (DASS): a reliable and suitable assessment tool for arthroscopic skill training
The results of this study indicate good validity and reliability of DASS for the assessment of the surgical performance of diagnostic knee arthroscopy during simulator training. Standardized training is recommended before arthroscopy surgery is considered in patients.
Validation of Virtual Reality Arthroscopy Simulator Relevance in Characterising Experienced Surgeons
Virtual reality (VR) simulation is particularly suitable for learning arthroscopy skills. Despite significant research, one drawback often outlined is the difficulty in distinguishing performance levels (Construct Validity) in experienced surgeons. Therefore, it seems adequate to search new methods of performance measurements using probe trajectories instead of commonly used metrics.

100 Years of Arthroscopy at Cantonal Hospital Aarau
A 100 years ago, the Swiss surgeon Dr. Eugen Bircher performed what were probably the first knee arthroscopies on patients at the Cantonal Hospital Aarau. Since then, arthroscopies of almost all larger joints have been established and are considered standard procedures. Cantonal Hospital of Aarau celebrated the occasion by providing residents an arthroscopy course including fundamental skills training and advanced workshop on the knee, shoulder, and hip. VirtaMed was proud to train junior surgeons on our ArthroS™ simulators alongside DePuy Synthes models.
Cadaver versus Simulator Based Arthroscopic Training in Shoulder Surgery
There are few studies that compare the cadaver dissections with the medical simulators in means of talent improvement. Therefore, the aim of this study is to find out if using cadaver dissections is still the golden standard for surgical training or using the medical simulators in surgery could replace cadaver dissections
The ASSET Global Rating Scale is a Valid and Reliable Adjunct Measure of Performance on a Virtual Reality Simulator for Hip Arthroscopy
The purpose of this study is to further evaluate the construct validity and interobserver reliability of a hip arthroscopy virtual simulator using the Arthroscopic Surgery Skill Evaluation Tool (ASSET) global rating scale.
Module-Based Arthroscopic Knee Simulator Training Improves Technical Skills in Naive Learners: A Randomized Trial
Module-based simulation training provides additional training time and improves technical skills in naive health science students. It is hoped that this effect can be preserved and applied to junior resident developing in a busy residency program.
Active vs Passive Haptic Feedback Technology in Virtual Reality Arthroscopy Simulation: Which is Most Realistic?
Virtual Reality (VR) simulators are playing an increasingly prominent role in orthopaedic training and education. Face-validity - the degree to which reality is accurately represented - underpins the value of a VR simulator as a learning tool for trainees. Despite the importance of tactile feedback in arthroscopy, there is a paucity for evidence regarding the role of haptics in VR arthroscopy simulator realism.
Simulation-based Arthroscopic Skills Using a Spaced Retraining Schedule Reduces Short-term Task Completion Time and Camera Path Length
The aim of this study was to investigate whether acquiring basic knee arthroscopic skills via a spaced retraining schedule could prevent skills deterioration and achieve further skills improvement.
Surgical Games: A Simulation-Based Structured Assessment of Orthopedic Surgery Resident Technical Skill
We describe the development and implementation of a timed, multitask, station-based Surgical Games to evaluate orthopedic resident surgical skills. (ArthroS™, VirtaMed AG, Schlieren, Switzerland)
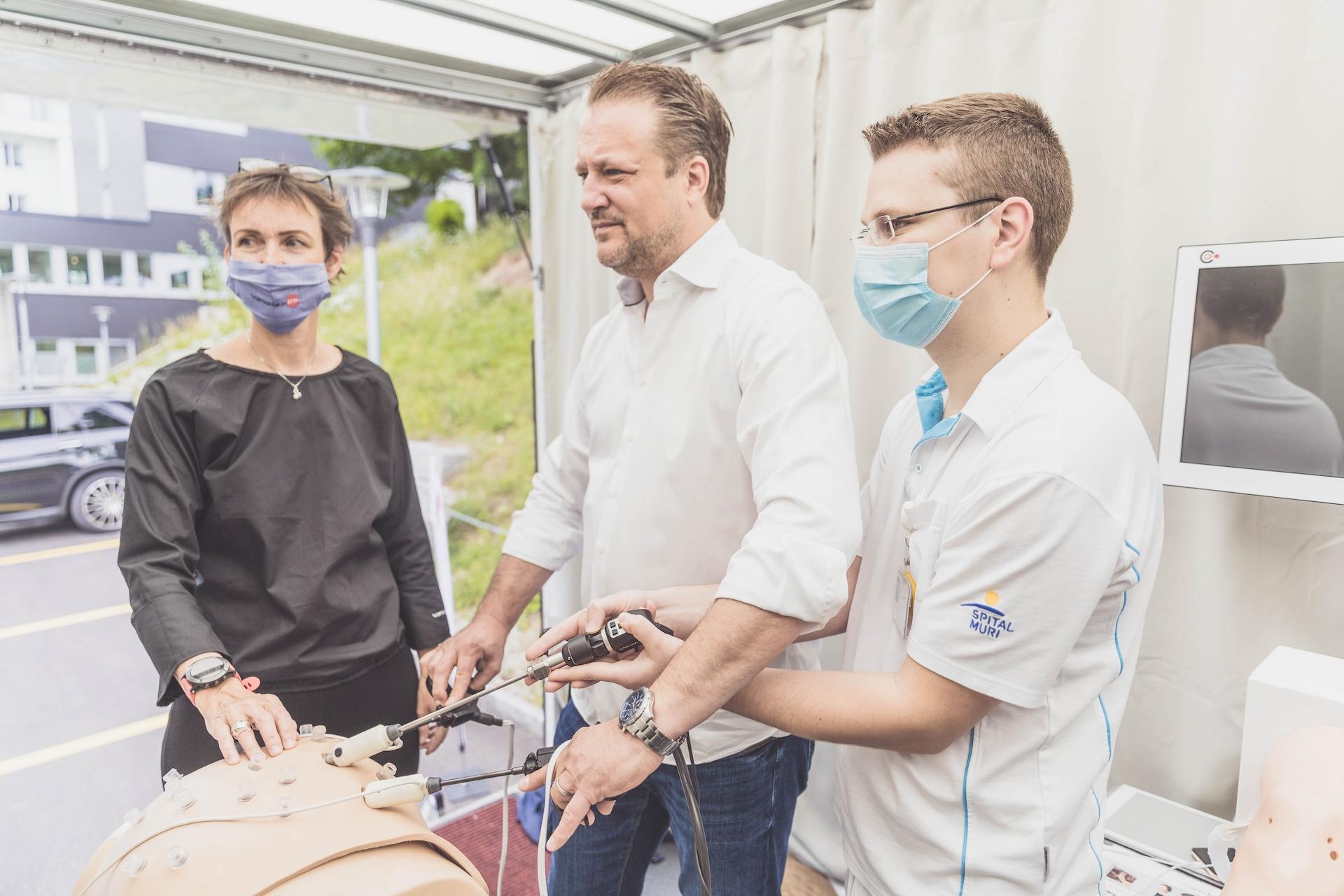

Medical Training Transported Across Switzerland
Amidst the coronavirus pandemic, VirtaMed could not be held back from providing medical training with new training solutions. Covid-19 has brought a number of limitations: Scientific conferences and training courses were cancelled, surgeries have been very limited, so there were hardly any opportunities to practice complex surgical procedures without risks.
Virtual Reality Simulator Improves the Acquisition of Basic Arthroscopy Skills in First-year Orthopedic Surgery Residents
Arthroscopy training using a virtual reality (VR) simulator is said to improve the training of orthopedic surgery residents, although it has never been evaluated in a large representative population of first-year residents.

Simulation skills lab at Cairo Kasr Al Aini School of Medicine
Ahmed El-Minawi, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the Cairo Kasr Al Aini School of Medicine, has recently inaugurated a new simulation and surgical skills lab (VESSALKA) at his department. Prof. El-Minawi is a strong proponent of simulation training and believes that trainees should develop hands-on expertise in a safe environment before starting to work with patients.

VirtaMed supports Perry Initiative
VirtaMed proudly supported the Perry Initiative Outreach Program's event at the Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, giving a unique opportunity for high school students to try their hands at orthopedic surgery. Mixed reality simulators allow students to try surgery in an accessible, risk-free environment - the perfect chance to inspire young women to be leaders in the exciting fields of Orthopedic Surgery and Engineering!

Why virtual reality simulation should be in every company's sales strategy
For companies launching new medical devices, the challenge is how to bring the commercial team and healthcare practitioners up to speed on unique product features. With a plethora of tools available, from e-learning to cadaver labs, where should high-fidelity virtual-reality simulation be used?
Validation of a Novel Hip Arthroscopy Simulator: Establishing Construct Validity
To assess the face, content and construct validity of a virtual reality hip arthroscopy simulator (ArthroS™, VirtaMed AG, Schlieren, Switzerland)
Lessons Taught by a Knee Arthroscopy Simulator About Participants in a European Arthroscopy Training Programme
Investigates the hypothesis that a theoretical and practical training course improves the scores achieved on an arthroscopy simulator task.
Validation of the Hip Arthroscopy Module of the VirtaMed Virtual Reality Arthroscopy Trainer
To assess the face, content and construct validity of a virtual reality hip arthroscopy simulator (ArthroS™, VirtaMed AG, Schlieren, Switzerland)
Validation of a Virtual Reality–Based Hip Arthroscopy Simulator
To assess construct and face validity of a novel virtual reality–based hip arthroscopy simulator using the previously validated Arthroscopic Surgery Skills Evaluation Tool (ASSET), metric parameters, and a questionnaire.
Efficacy of an Arthroscopic Virtual Based Simulator for Orthopedic Surgery Residents by Year in Training
Determine the utility of the ArthroS™ arthroscopic simulator for orthopedic trainees based on their level of training (to determine at what point in training the simulator offers the most benefit for trainees).
Efficacy of standardized training for arthroscopic motor skills
Most studies demonstrated, that training on a virtual reality based arthroscopy simulator leads to an improvement of technical skills in orthopaedic surgery. However, how long and what kind of training is optimal for young residents is unknown. In this study we tested the efficacy of a standardized, competency based training protocol on a validated virtual reality based knee- and shoulder arthroscopy simulator.
Knee, Shoulder, and Fundamentals of Arthroscopic Surgery Training: Validation of a Virtual Arthroscopy Simulator
Purpose: To validate the knee, shoulder, and virtual Fundamentals of Arthroscopic Training (FAST) modules on a virtual arthroscopy simulator via correlations with arthroscopy case experience and postgraduate year.
Validation of a virtual reality-based simulator for shoulder arthroscopy
This study was to determine face and construct validity of a new virtual reality-based shoulder arthroscopy simulator which uses passive haptic feedback.
Asymmetry in Dominant / Non-Dominant Hand Performance Differentiates Novices from Experts on an Arthroscopy Virtual Reality Serious Game
Safe and effective arthroscopic surgery requires ambidextrous motor skills. The current study examined dominant versus non-dominant hand performance on a virtual reality serious game in a group of expert arthroscopic surgeons (n=15) compared to a group of orthopedic surgery residents (n=10).
Comparison Of Three Virtual Reality Arthroscopic Simulators As Part Of An Orthopedic Residency Educational Curriculum
Orthopedic education continues to move towards evidence-based curriculum in order to comply with new residency accreditation mandates. There are currently three high fidelity arthroscopic virtual reality (VR) simulators available, each with multiple instructional modules and simulated arthroscopic procedures. The aim of the current study is to assess face validity, defined as the degree to which a procedure appears effective in terms of its stated aims, of three available VR simulators.
Which Global Rating Scale? A Comparison of the ASSET, BAKSSS, and IGARS for the Assessment of Simulated Arthroscopic Skills
With the move to competency-based models of surgical training, a number of assessment methods have been developed. Of these, global rating scales have emerged as popular tools, and several are specific to the assessment of arthroscopic skills. Our aim was to determine which one of a group of commonly used global rating scales demonstrated superiority in the assessment of simulated arthroscopic skills.
Evaluation of a virtual-reality-based simulator using passive haptic feedback for knee arthroscopy
Simulator training in orthopaedics is still in its infancy. The aim of this study is to determine face and construct validity of a new virtual reality simulator (VirtaMed ArthroS™) for diagnostic and therapeutic knee arthroscopy by analysis of simulator metrics of participants with varying arthroscopy experience.
Virtual Reality Simulator for Training on Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate with 980 nm Diode Laser and Learning Curve of the Technique
The utility of a virtual reality simulator for training of the photoselective vaporization of the prostate with diode laser was studied.
Virtual reality simulator for training urologists on transurethral prostatectomy
As a new method of training on transurethral prostatectomy skills, training of TURP using a virtual simulator can help urologists improve their surgical skills and safety. Therefore, the application of the TURPSim™ system in education and training of urologic surgery is warranted.
Face validity, construct validity and training benefits of a virtual reality TURP simulator
Virtual reality (VR) surgical simulators provide repetitive practice and performance feedback without requiring supervision in a safe environment. Simulators have the potential to shorten the learning curve for complex surgical procedures, create skills which transfer to the operating room and therefore decrease the incidence of future complications. Experts resected a significantly greater percentage of prostate per minute [...] and had significantly less active diathermy time without tissue contact [...] than novices.
Visual Control Strategies of Surgeons: A Novel Method of Establishing the Construct Validity of a Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Surgical Simulator
Significant differences between experts and novices in both performance and visual control strategy were observed. The study of visual control strategies may be a useful adjunct, alongside measurements of motor performance, providing a novel method of assessing the construct validity of surgical simulators.
Learning effects using a TURP simulator: Assessing changes in visual control and performance
Surgical simulators afford trainees the chance to practice skills in a safe environment and without the need for supervision. Although they have been proposed to shorten the learning curve for complex surgical skills, there is concern that they do not prepare trainees for the demanding conditions of the operating room. Research in skill learning (including surgical skills) has shown that experts and novices can be distinguished by differences in their visual control strategies, with experts using fewer fixations of a longer duration. The aim of this study was to assess the learning benefits of a TURP simulator by examining, not only changes in novice performance, but also changes in their visual control.
- Technology & Instruments: Surgical Education & Skills Assessment/Ureteroscopy II Moderated Poster
Simulator Based Development of “Trans-Urethral Resection of Prostate” Skills and implementation of “Global Rating Scale” Evaluation System in Urology Postgraduate training
After the introduction of simulators in urology, education in urology has evolved significantly. Specially in endourology, development of Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) skills are shifted from “direct on patient” to simulator based learning. we evaluated the development of TURP procedure skills based on virtual reality simulator (VirtaMed | UroSim™) and assessment of skills based on Global Rating Scale (GRS) evaluation system.
- Poster presented at the World Congress of Endourology (WCE), Vancouver, September 2017
Evaluation of the educational value of a virtual reality TURP simulator according to a curriculum-based approach
This study aimed to evaluate the place of the TURPsim (VirtaMed) within a urologic residency training curriculum, including training needs analysis (TNA) and investigating its validity.
Construct validity of UroSim® simulator for learning transurethral resection of bladder tumor
There is an increasing trend to incorporate Simulator-based training in urology residency programs. The study was designed to determine the construct validity of UroSim® for that we compared the performance of transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) between experts and novices.
Preliminary Experience with Virtual Reality Simulation vs. Animal Model for Hysteroscopic Myomectomy Training
The HystSim™ Virtual Reality hysteroscopic trainer was felt to be at least equal to the ‘‘gold standard’’ pig bladder model for training in hysteroscopic myomectomy with the additional advantages of reproducibility and measurement of results. Further studies comparing modalities and relating results to operating room performance are warranted.
Establishing construct validity of a virtual-reality training simulator for hysteroscopy via a multimetric scoring system
The aims of this study are to determine construct validity for the HystSim™ virtual reality (VR) training simulator for hysteroscopy via a new multimetric scoring system (MMSS) and to explore learning curves for both novices and experienced surgeons.
Evaluation of a new virtual-reality training simulator for hysteroscopy
Face validity has been established for a new hysteroscopic surgery simulator. Potential trainees and trainers assess it to be a realistic and useful tool for the training of hysteroscopy. Further systematic validation studies are needed to clarify how this system can be optimally integrated into the gynecological curriculum.
Hysteroscopic Resection on Virtual Reality Simulator: What do We Measure?
The objective was to compare results of two groups of population (novices and experts) on a virtual reality simulator of hysteroscopy resection for different metrics and for a multimetric score to assess its construct validity.
Assessment of a high-fidelity mobile simulator for intrauterine contraception training in ambulatory reproductive health centres
Little is known about the utility of simulation-based training in office gynaecology. The objective of this cross-sectional study was to evaluate the self-reported effectiveness and acceptability of the PelvicSim™ (VirtaMed), a highfidelity mobile simulator, to train clinicians in intrauterine device (IUD) insertion.
Evaluation of the HystSim™-virtual reality trainer: an essential additional tool to train hysteroscopic skills outside the operation theater
Minimally invasive surgery is a major pillar of gynecological surgery. However, there are very few training opportunities outside the operation theater (OR) due to the cost and equipment requirements of organ simulators, virtual reality trainers (VRT) are promising tools to fill this gap.
Standardizing Hysteroscopy Teaching: Development of a Curriculum Using the Delphi Method
Hysteroscopy is performed often and in many indications but is challenging to learn. Hands-on training in live patients faces ethical, legal, and economic obstacles. Virtual reality simulation may hold promise as a hysteroscopy training tool. No validated curriculum specific in hysteroscopy exists. The aim of this study was to develop a hysteroscopy curriculum, using the Delphi method to identify skill requirements.
Integration and Validation of Hysteroscopy Simulation in the Surgical Training Curriculum
The primary objective of our study was to test the construct validity of the HystSim hysteroscopic simulator to determine whether simulation training can improve the acquisition of hysteroscopic skills regardless of the previous levels of experience of the participants. The secondary objective was to analyze the performance of a selected task, using specially designed scoring charts to help reduce the learning curve for both novices and experienced surgeons.
Operative and diagnostic hysteroscopy: A novel learning model combining new animal models and virtual reality simulation
Hysteroscopy is one of the most common gynaecological procedure. Training for diagnostic and operative hysteroscopy can be achieved through numerous previously described models like animal models or virtual reality simulation. We present our novel combined model associating virtual reality and bovine uteruses and bladders.

Supporting medical education during Covid
A 94% satisfaction rating makes VirtaMed's Support Team stand out as a global leader when it comes to helping our customers continue their medical education! Alberto Nonini, Head of Service & Support, shares his insights into supporting customers through the COVID-19 period.
Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate: Simulation-Based Training Curriculum and Validation
To evaluate the face, content, and construct validity of a novel virtual reality simulator for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) and to assess its feasibility and acceptability as a training model.
Simulation Training for Embryo Transfer: Findings from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine Embryo Transfer Certificate Course
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine Embryo Transfer Certificate Course data analysis demonstrates the effectiveness of simulator-based ET training for REI fellows across the 3 years of training, regardless of prior experience with live ET.
Construct validity of UroSim® simulator for learning transurethral resection of bladder tumor
There is an increasing trend to incorporate Simulator-based training in urology residency programs. The study was designed to determine the construct validity of UroSim® for that we compared the performance of transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) between experts and novices.
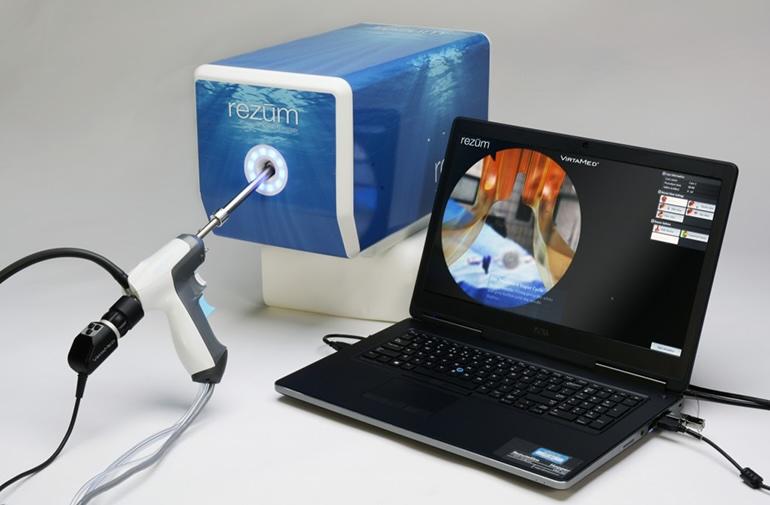
Rezum
The Rezum system is a device that utilizes radiofrequency energy to create thermal energy in the form of water vapor to destroy and eliminate excessive prostatic tissue growth caused by Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). Using procedure videos from 197 different patients in the Rezum II pivotal study, we developed five very representative simulated procedures from easy to most challenging – “most challenging” is primarily related to differences in anatomy.