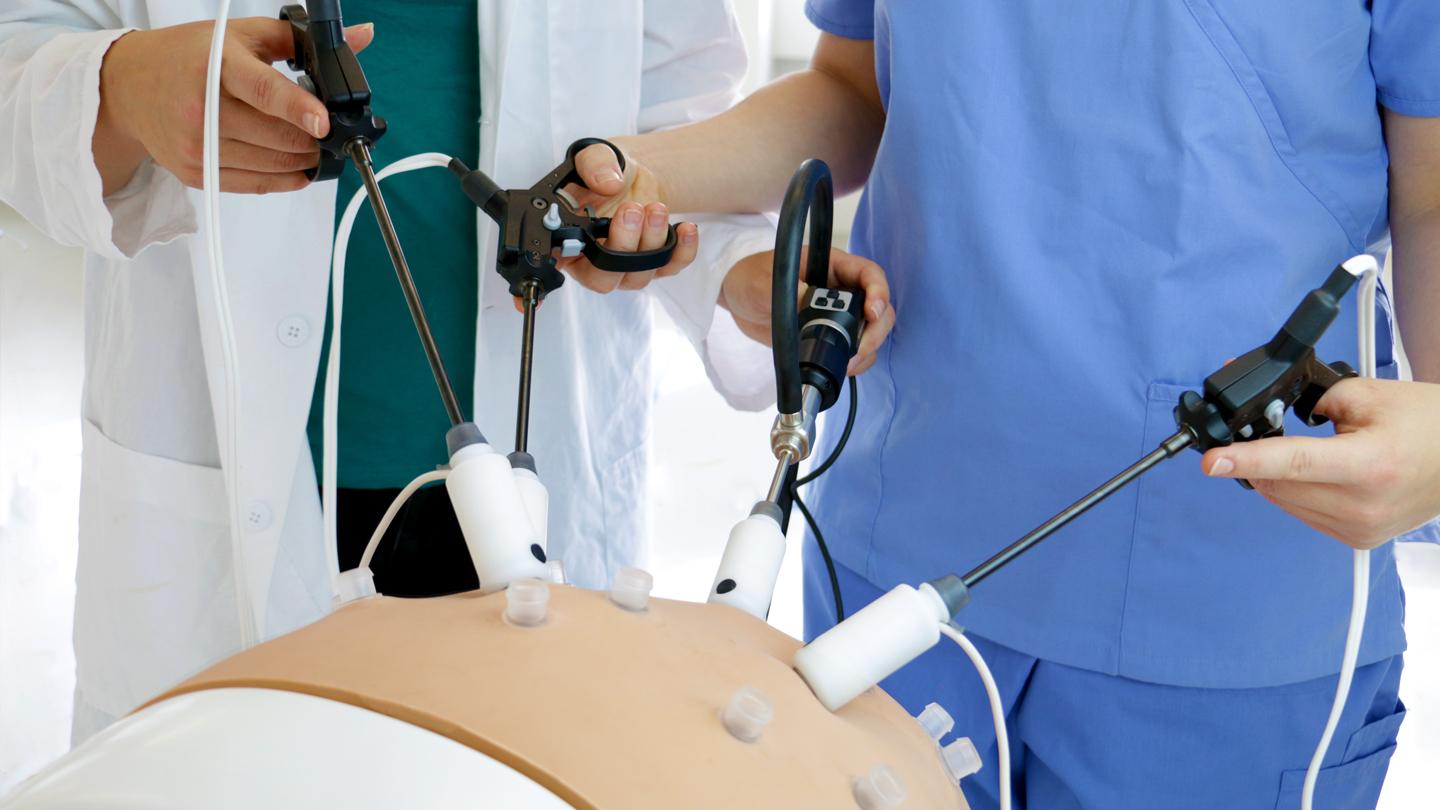
LaparoS™
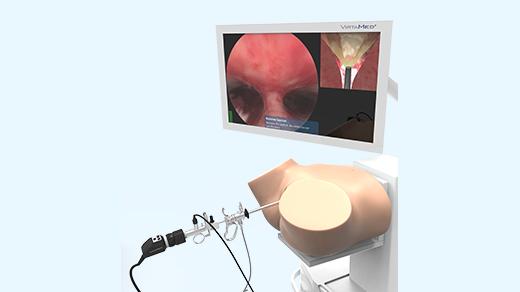
Comprehensive laparoscopy training simulator with unmatched realism: real graphics, real instruments, real feel. Prepare for the operating room with precision and confidence using our state-of-the-art mixed reality technology.
LaparoS™ Simulation modules
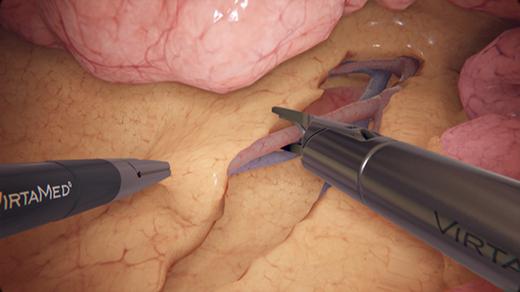
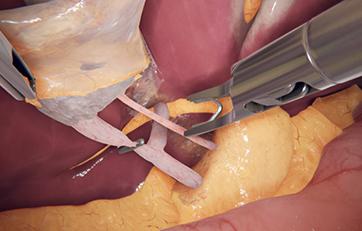
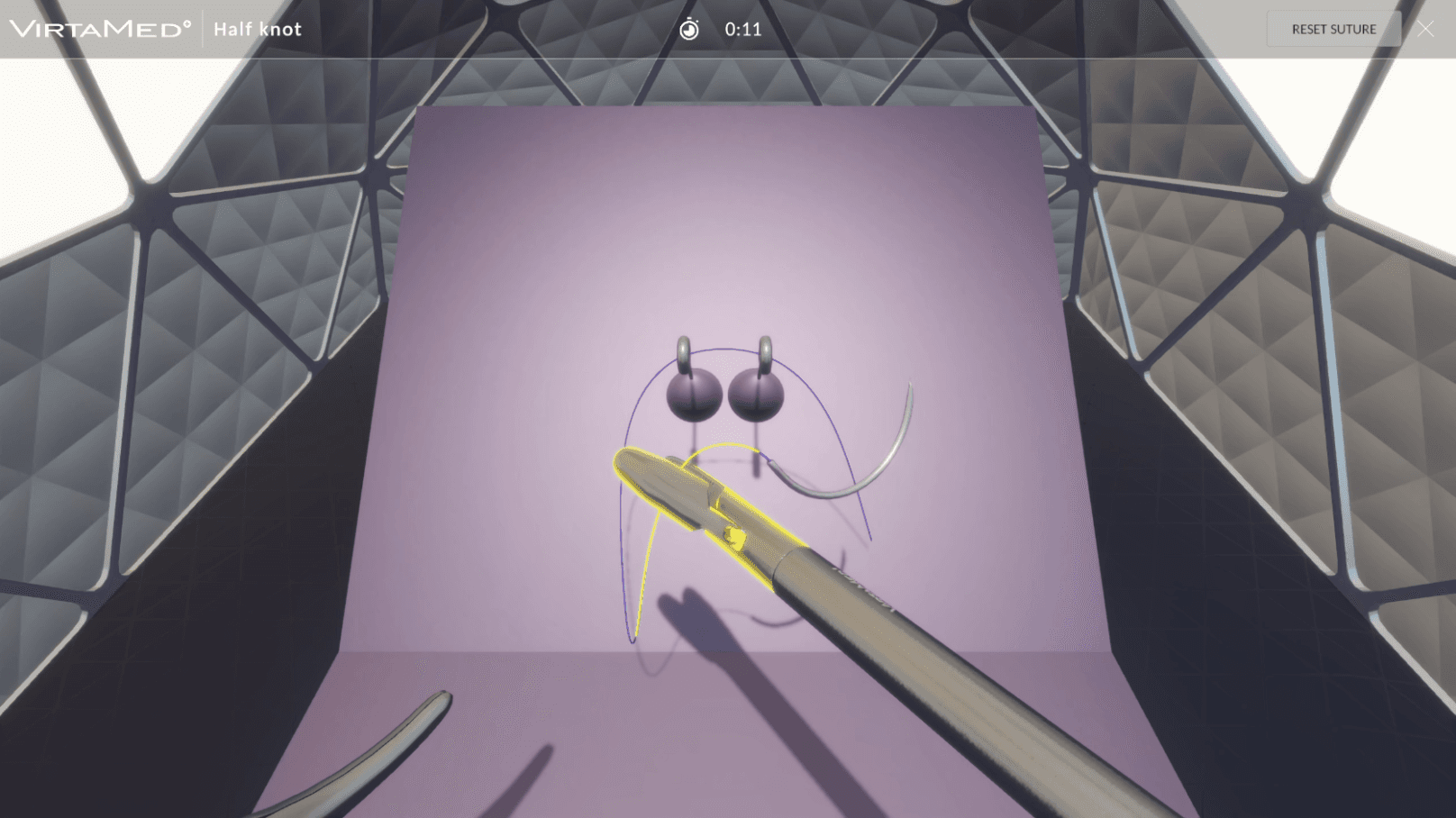
LaparoS™ Suturing
Cumulative and step-by-step training cases focusing on specific skills for safe needle manipulation and intracorporeal knot tying (half knot, square knot, and surgeon’s knot). Using two needle holders, or a grasper and a needle holder, trainees can hone their skills with precision and confidence, ultimately enhancing their proficiency and readiness for certification, such as the GESEA MIGS.
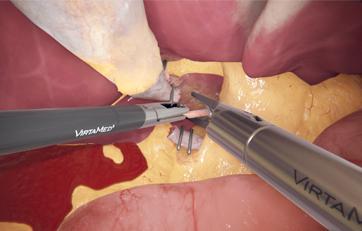
LaparoS™ Advanced suturing
Developed with leading surgeons, this module refines advanced suturing skills for procedures like ventral hernia repair and vaginal cuff closure. With progressive difficulty levels and real-time performance metrics, it enhances precision, efficiency, and technique. Designed for general and gynecological surgeons, it supports training for certifications like FLS and GESEA MIGS.

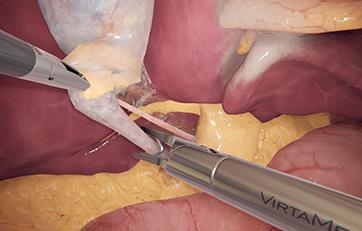
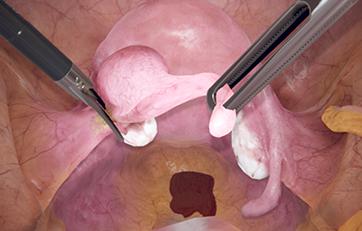
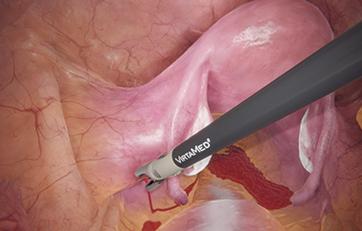
LaparoS™ Gynecological laparoscopy
This module offers condensed diagnostic and surgical training cases for laparoscopy with highly realistic scenarios derived from both fertility surgery and other gynecological procedures. It can be combined with the GynoS™ platform for a full OB-GYN offering.
LaparoS™ Simulation platforms

LaparoS™ Skills progression
General Surgery
Gynecological Laparoscopy
VirtaMed services
Connect
VirtaMed Connect is your all-in-one online platform, securely storing course data in the cloud for 24/7 access. With Connect, course directors effortlessly track resident progress, evaluate cohort and individual performance, and deliver targeted feedback. Plus, it simplifies the implementation of new courses, saving you valuable time while monitoring student progress.
Proficiency development
Technology is transforming medical education and training. VirtaMed's Training and Education team is skilled at developing training programs and optimally integrating active learning solutions into the learning journey.
Service & support
With a Net Promotor Score of more than 90, VirtaMed Services and Support team provides ongoing support, with a proven track record to resolving customer issues swiftly and effectively, ensuring seamless and hassle-free technology experiences.
Supporters
Factsheets & validation
Get more details about the most realistic laparoscopic simulator.